

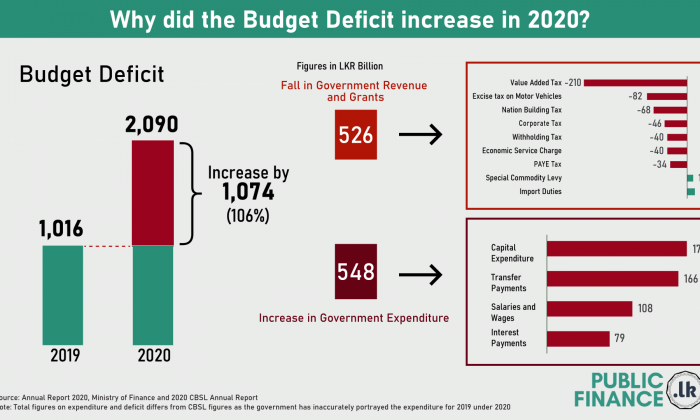
Sri Lanka’s budget deficit has doubled between the period of 2019 and 2020. The budget deficit increased from LKR 1,016 billion in 2019 to LKR 2,090 billion in 2020, which is an increase of LKR 1,074 billion. The increase in the budget deficit can be attributable to LKR 526 billion decline in revenue and LKR 548 billion increase in expenditure.
Fall in the government revenue
The decline in the government revenue is due to a reduction in the revenue collected mainly from several taxes such as Value Added Tax (LKR 210 billion), Excise duty on Motor Vehicle (LKR 82 billion), Nation Building Tax (LKR 68 billion), Corporate tax (LKR 46 billion), Withholding tax (LKR 40 billion), Economic Service Charge (LKR 40 billion), and PAYE tax (LKR 34 billion). However, there has also been a moderate increase in tax revenue from Special Commodity Levy (LKR 12 billion) and Import Duties (LKR 16 billion). For details on the change in all revenue items see Exhibit 1
It is important to note that there were also several key tax policy changes in late 2019 which contributed to the decline in revenue. The key tax policy changes were;
In addition, the government also banned the import of most motor vehicles from April 2020, which could have led to a significant reduction in the excise duty on motor vehicles.
Increase in the government expenditure
The increase in government expenditure is mainly due to increase in; capital expenditure (LKR 176 billion), Transfer Payments (LKR 166 billion), Salaries and Wages (LKR 108 billion) and Interest Payment (LKR 79 billion). For details on the change in all expenditure see Exhibit 2
It is important to note the government had allocated LKR 35 billion for the provision of COVID-19 relief assistance through the State Ministry of Samurdhi in the 2021 Budget which was presented in November 2020. The government also recruited 160,000 unskilled and unemployed graduates that cost LKR 65 billion as additional expenses per annum (see https://publicfinance.lk/en/topics/New-Government-Recruitment-Schemes:-An-increased-burden-on-taxpayers-1620677894)
Note: 2019 and 2020 budget deficit figures reported by the CBSL Annual Report are inconsistent with the previous years, hence cannot be used for comparison across years. Please refer our previous insight for more details on this; https://publicfinance.lk/en/topics/2020-Records-the-Highest-Budget-Deficit-Since-1982-1620901757
*A budget deficit occurs when the government expenditure is higher that the government revenue.
Source: Annual Report (2020), Central Bank of Sri Lanka
Exhibit 1: Government Revenue and Grants (2019 and 2020)
All figures in LKR Million
|
Category |
2019 |
2020 Provisional |
Decline in 2020 |
|
Tax Revenue |
1,734,925 |
1,216,542 |
518,383 |
|
Taxes on Foreign Trade |
280,965 |
312,334 |
-31,369 |
|
Imports |
98,427 |
114,183 |
-15,756 |
|
Import Duty (gross) |
98,427 |
114,183 |
-15,756 |
|
less Duty Rebate |
- |
- |
- |
|
PAL/RIDL/SCL/Other |
182,538 |
198,151 |
-15,613 |
|
Taxes on Domestic G&S |
843,355 |
555,718 |
287,637 |
|
GST/VAT |
443,877 |
233,786 |
210,091 |
|
Domestic GST/VAT |
273,963 |
148,061 |
125,902 |
|
GST/VAT on imports |
169,914 |
85,725 |
84,189 |
|
Excise Tax |
399,478 |
321,932 |
77,546 |
|
Excise Tax on Liquor |
115,443 |
120,990 |
-5,547 |
|
Excise Tax on tobacco/cigarettes |
87,367 |
94,345 |
-6,978 |
|
Excise Tax on petroleum |
61,740 |
53,111 |
8,629 |
|
Excise Taxes on MV and other |
134, |
53,486 |
81,441 |
|
National Security Levy |
- |
- |
- |
|
License Fees |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
|
Taxes on Net Income and Profits |
427,700 |
268,249 |
159,451 |
|
Corporate |
261,089 |
214,819 |
46,270 |
|
Non-Corporate |
11,514 |
13,517 |
-2,003 |
|
Tax on Interest |
50,351 |
9,989 |
40,362 |
|
Capital Gains Tax |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
|
Stamp Duty/Cess Levy/SRL/NBT/DL/TL |
182,905 |
80,241 |
102,664 |
|
Debits Tax |
- |
|
- |
|
Non Tax Revenue |
155,974 |
151,417 |
4,557 |
|
Current Revenue |
155,974 |
151,417 |
4,557 |
|
Property Income |
46,404 |
60,984 |
-14,580 |
|
Rent |
4,727 |
12,055 |
-7,328 |
|
Interest |
13,819 |
7,297 |
6,522 |
|
Profits and Dividends |
27,857 |
17,624 |
10,233 |
|
National Lottery |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
|
Central Bank Profit transfers |
- |
24,009 |
24,009 |
|
Social Security Contributions |
28,985 |
32,417 |
-3,432 |
|
Fees and Administration Charges |
73,884 |
47,370 |
26,514 |
|
Other |
6,701 |
10,646 |
-3,945 |
|
Capital Revenue |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total Revenue |
1,890,899 |
1,367,960 |
522,939 |
|
Grants |
7,909 |
5,348 |
2,561 |
|
Total Revenue |
1,898,808 |
1,373,308 |
525,500 |
Exhibit 2: Government Expenditure (2019 and 2020)
All Figures in LKR Million
|
Years |
2019 |
2020 |
Increase in 2020 |
|
1. Recurrent Expenditure |
2,424,582 |
2,671,786 |
247,204 |
|
1.1 Expenditure on Goods and Services |
848,278 |
974,351 |
126,073 |
|
Salaries and Wages |
686,452 |
794,158 |
107,706 |
|
Civil Administration |
420,300 |
509,555 |
89,255 |
|
Defence |
266,152 |
284,603 |
18,451 |
|
Other Purchases of Goods and Services |
161,826 |
180,193 |
18,367 |
|
Civil Administration |
82,489 |
100,006 |
17,517 |
|
Defence |
79,338 |
80,187 |
849 |
|
Provision for Under Expenditure |
- |
- |
- |
|
1.2 Interest Payments |
901,353 |
980,302 |
78,949 |
|
Foreign |
233,970 |
266,679 |
32,709 |
|
Domestic |
667,383 |
713,623 |
46,240 |
|
1.3 Transfer Payments |
551,524 |
717,133 |
165,609 |
|
Households |
456,241 |
610,486 |
154,245 |
|
Sub National Governments |
- |
- |
- |
|
Non-financial Public Enterprises |
26,153 |
17,712 |
-8,441 |
|
Institutions and Other |
69,130 |
88,936 |
19,806 |
|
2. Capital Expenditure |
619,069 |
795,368 |
176,299 |
|
2.1 Acquisition of Fixed Capital Assets |
385,366 |
483,543 |
98,177 |
|
2.2 Capital Transfers |
239,688 |
307,917 |
68,229 |
|
Institutions |
200,172 |
254,384 |
54,212 |
|
Non-financial Public Enterprises |
20,704 |
34,365 |
13,661 |
|
Sub National Governments |
18,812 |
19,168 |
356 |
|
Abroad |
1,951 |
N/A | N/A |
|
Provision for Under Expenditure |
- |
- |
- |
|
2.3 Other |
-5,985 |
3,907 |
9,892 |
|
3. Lending Minus Repayments |
-4,933 |
-3,552 |
1,381 |
|
3.1 Net Lending through Advance Accounts |
1,172 |
-529 |
-1701 |
|
3.2 Lending to Public Enterprises |
12,166 |
16,405 |
4,239 |
|
3.3 Loan Repayments in Public Enterprises |
-18,271 |
-19,429 |
-1,158 |
|
3.4 Restructuring Expenditure |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total |
2,915,291 |
3,463,602 |
548,311 |
Source: Annual Report (2020), Central Bank of Sri Lanka